Ribs are thin support features frequently found in plastic injection moulded part designs. They are often used strategically to replace thick wall sections to avoid sink marks, warp, and voids, and help improve overall part function. In some cases, ribs also act as decorative features.
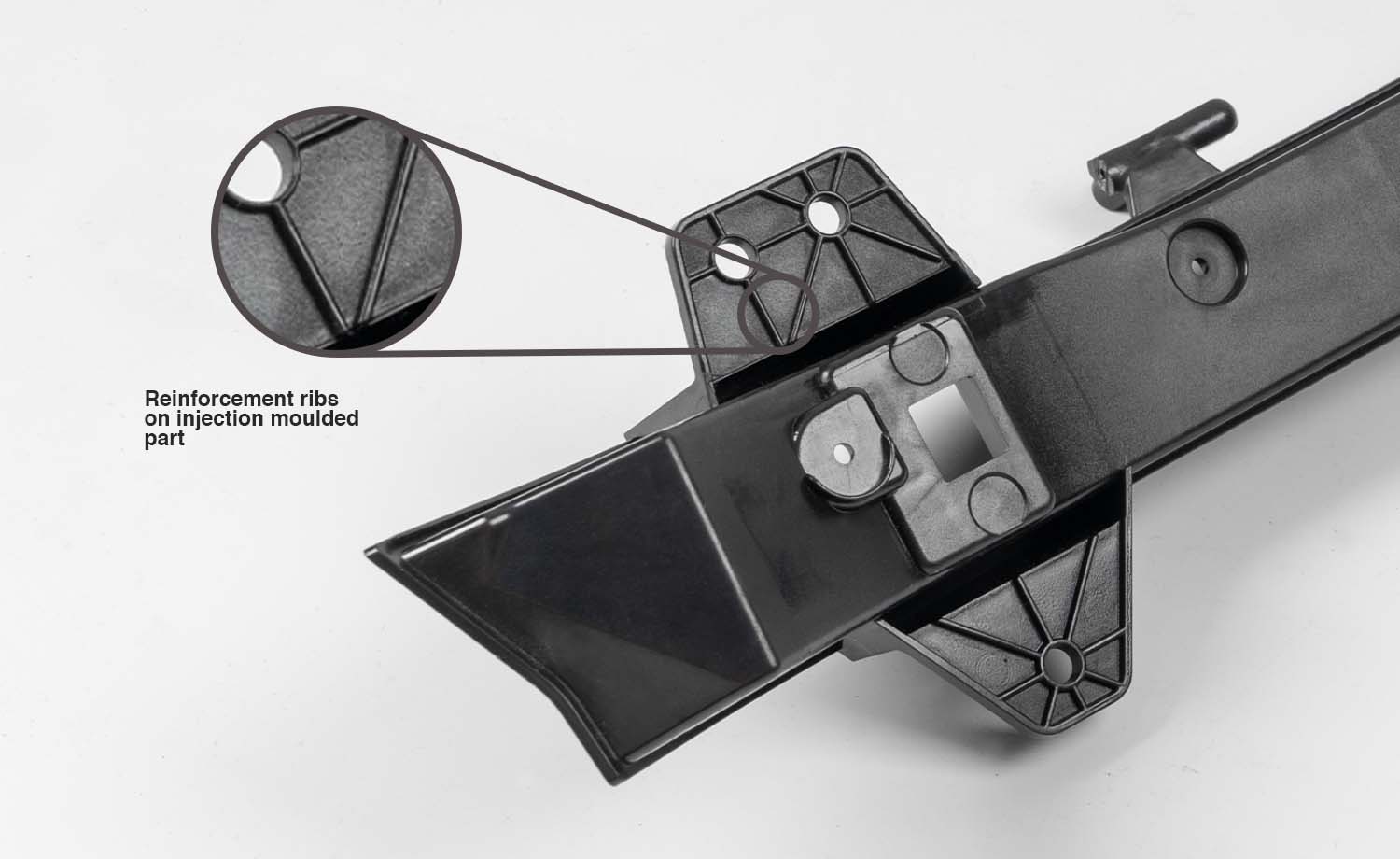
To fully benefit from the capabilities of rib features, it is important that your injection mould model is designed according to a number of recommendations. This article covers the scenarios in which ribs should be used in injection moulding and offers a comprehensive guide to the best design practices for rib features.
We’ve listed several scenarios below in which rib features work particularly well for:
Rib Height
Rib height should not exceed 3 times the nominal wall thickness. Ribs that are too long will increase the difficulty of injection moulding, causing problems like voids and sink marks. Ideally, you want to keep ribs as short as possible while still being functional.
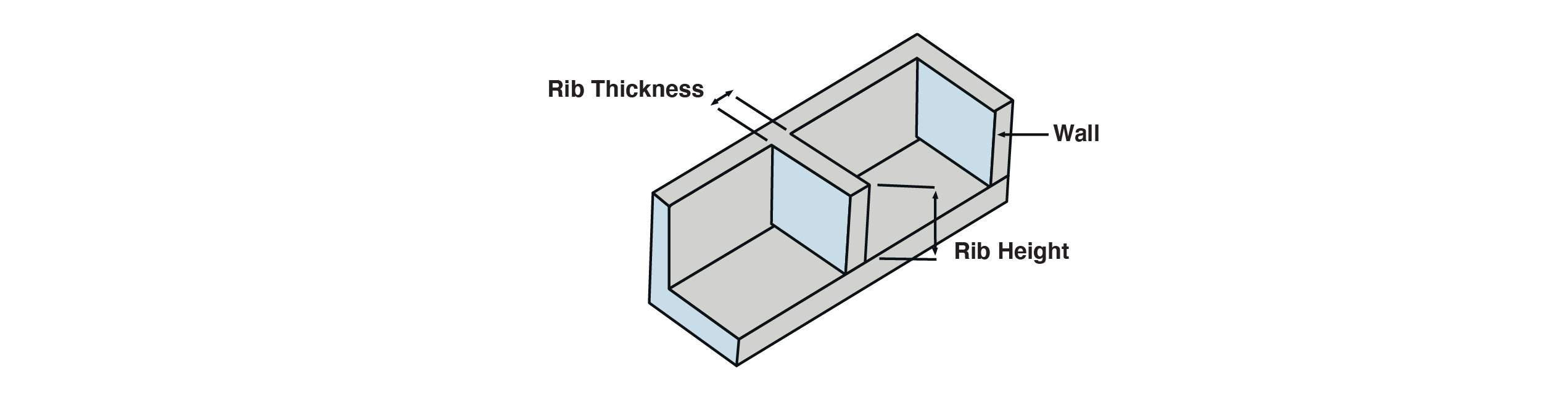
Rib Thickness
As a general rule of thumb, ribs should not be thicker than 60% of the nominal wall thickness. Maintaining an appropriate rib-to-wall ratio is essential to prevent issues such as air bubbles, shrinkage patterns and stress concentration. Ultimately, avoid thick ribs whenever possible.
Rib Radii
The base of a rib should always be rounded with a radius to prevent an area of concentrated stress in the part. This radius should typically be 0.5 to 1 times the thickness of the part wall to increase rib strength.
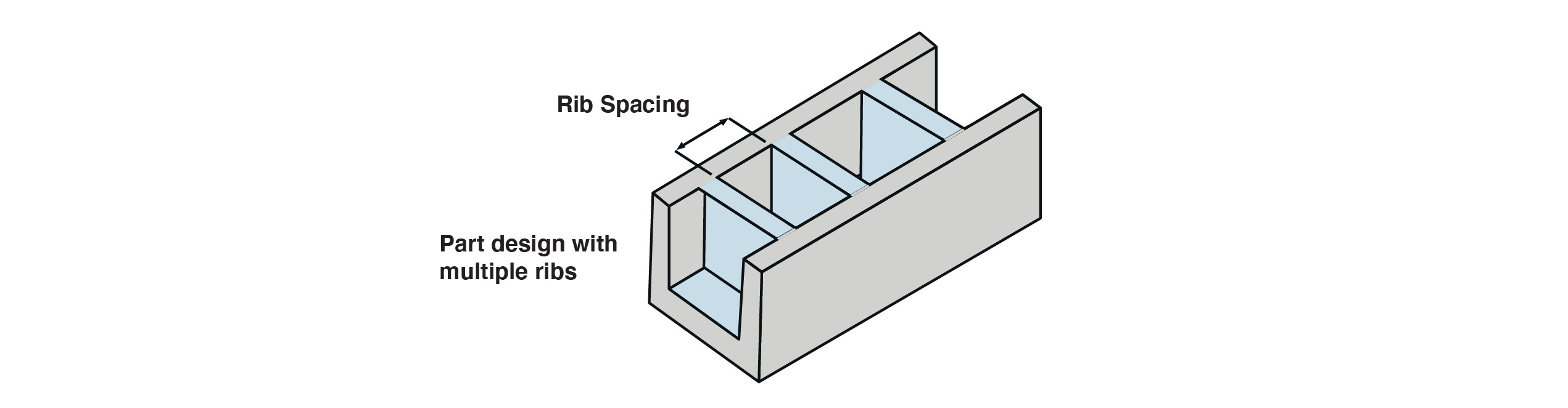
Rib Spacing
When incorporating multiple ribs, it’s recommended to space them out at least 2 to 3 times the nominal wall thickness. It’s essential to leave adequate space, as ribs placed too close together can create cooling issues, which can increase cycle times and sink risk.
Rib Draft
A draft angle of at least 0.5 degrees on each side should be incorporated to allow for easy part ejection from the mould. Only crush ribs should be made without a draft angle.
| Rib Height | Should not exceed 3X the nominal wall thickness |
|---|---|
| Rib Thickness | Should not exceed 60% of the nominal wall thickness |
| Rib Radii | Should be 0.5 – 1X the nominal wall thickness |
| Rib Spacing | Should be 2 – 3X the nominal wall thickness |
| Rib Draft | Should be at least 0.5 degrees on each side |
Incorporating ribs is a critical feature that should be carefully considered for nearly all enclosures, housings, casings and other plastic parts where wall thickness is important. In order to ensure successful moulding of rib designs, it is important to closely follow best design practices.
Use the Rib Design Guidelines above to help design your parts for manufacturing then export your 3D CAD files in an STEP format. Submit your drawings to our site contact form and our engineering team will get back with a quote and comprehensive DFM (design for manufacturing) feedback.
