Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an industrial 3D printing process printing process ideal for manufacturing end-use parts. Unlike other additive manufacturing processes, such as SLA and FDM, SLS does not require support structures, allowing for greater design freedom. For this reason, it is also one of the easier 3D printing technologies to design for.
SLS produces functional plastic parts with isotropic mechanical properties that can be used for detailed prototyping or end-use low-volume production parts.
To fully utilize the capabilities of this technology, it is important that your 3D model is designed according to a number of recommendations. In this article, we offer a comprehensive guide to the best design practices for SLS 3D Printing. It covers the characteristics of the process, our capabilities, design guidelines, summary of best SLS design practices and cost reduction tips.
In SLS, a laser selectively sinters polymer powder particles, fusing them together and building parts layer-by-layer. The unsintered powder provides the part with all the necessary support, hence support structures are not needed.
Disadvantages of the SLS Process
| Maximum Build Size | 400 x 400 x 450mm |
|---|---|
| Resolution | ±0.2mm |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.3% (with a lower limit of ±0.3 mm) |
| Materials | Nylon 12, Nylon 12+GF, TPU |
| Surface Structure | Grainy structure |
| Support | Not required |
Wall Thickness
For SLS designs, walls that are designed too thick or thin are at risk of warpage. To ensure successful print, walls should be at least 0.7mm. At HLH, 1mm wall thickness is recommended.

Holes
The deeper the hole, the larger the hole diameter should be. All holes should be larger than 1mm in diameter. Blind holes — holes that do not extend completely through the wall — should be designed with an escape hole to allow for powder removal.
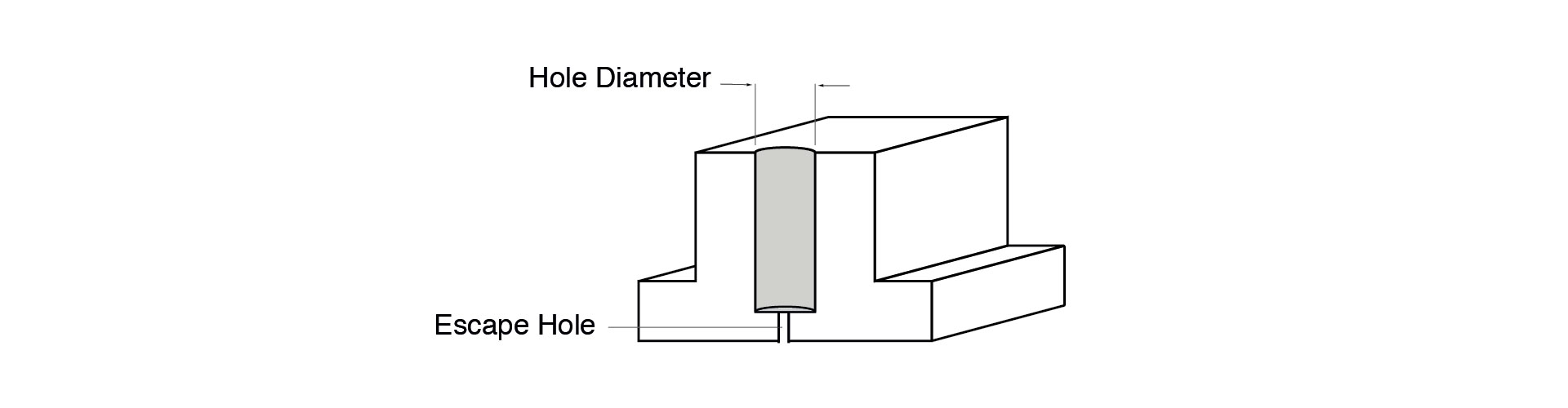
Hollow Parts
For hollow parts and designs containing blind holes, it is important to include more than one escape hole in your design to improve the ease of powder removal. At HLH, we recommend a minimum hole diameter of 3.5mm.
Slots
What size to design a slot is determined by the depth or thickness of the wall. We recommend a minimum slot size of 0.5mm. Keep in mind that if the depth or wall thickness is over 2mm, a minimum slot size of 0.5mm will be insufficient, and the print may fail.

Pins
The main difficulty when designing pins for SLS is the risk of small pins being too fragile and breaking off during post-processing. The minimum pin diameter is 0.8mm. The taller the pin, the greater its risk of breaking; increasing its diameter will give a tall pin more strength.
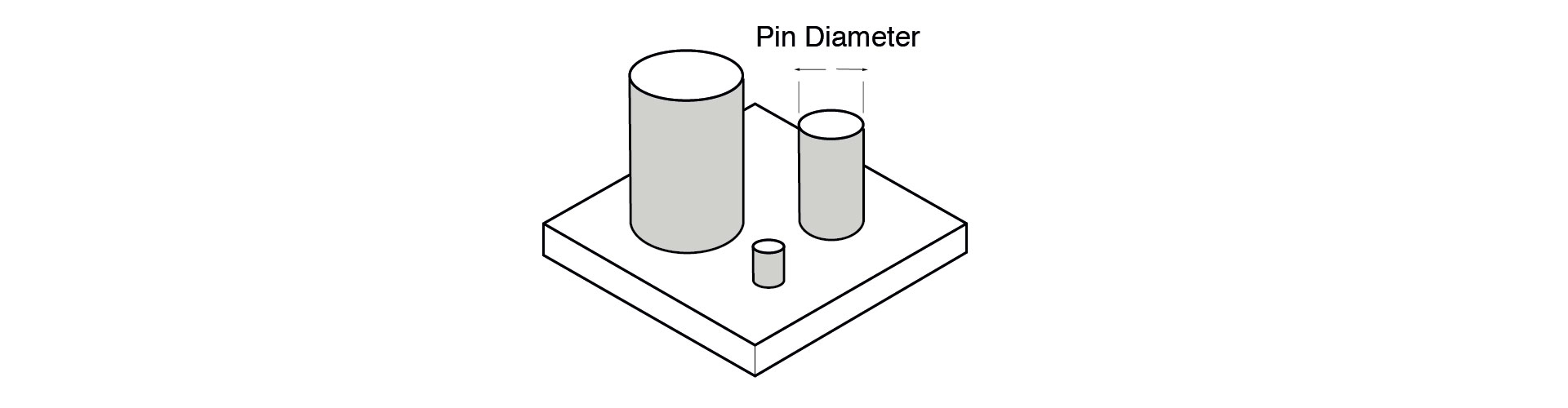
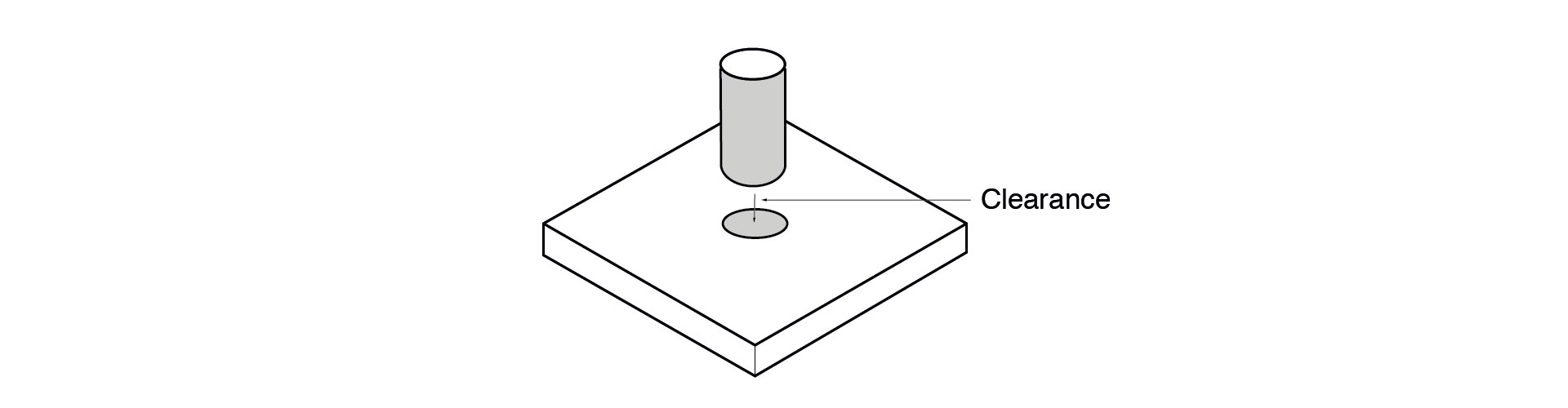
Mating Parts
For SLS parts, adequate clearances must be designed between mating parts to prevent the assembly from fusing together into a single solid unit. To avoid this, models must be designed with a minimum clearance of 0.5mm.
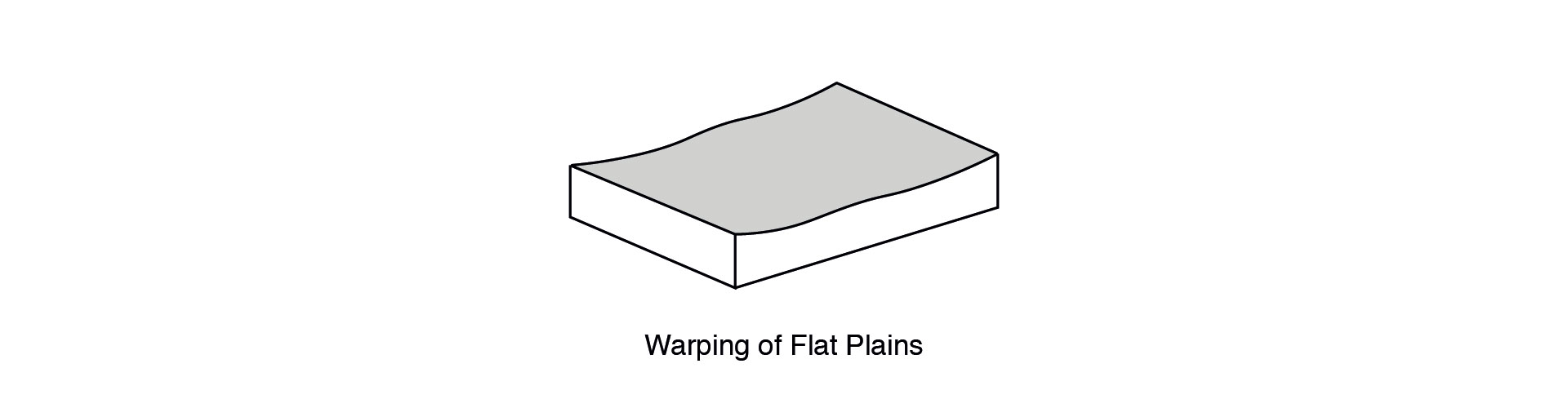
Large, Flat Surfaces
Large, flat plains are susceptible to unpredictable ‘warping.’ Hence, such designs are not recommended. If they are a crucial feature of a part, ribs can be added to provide support; however, this may not always solve the problem, as such, such surfaces should be avoided whenever possible.
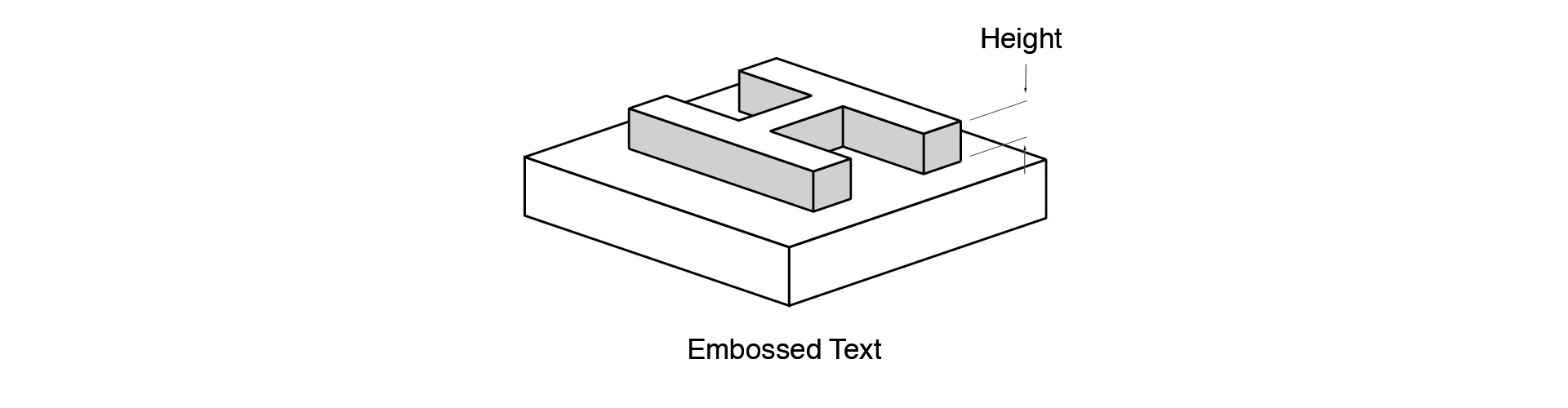
Embossed Features
Embossed features must be designed using a minimum height, otherwise, it may not appear visible. They should be designed with a height of at least 1mm. To ensure such details come out nicely, make them larger than the indicated.
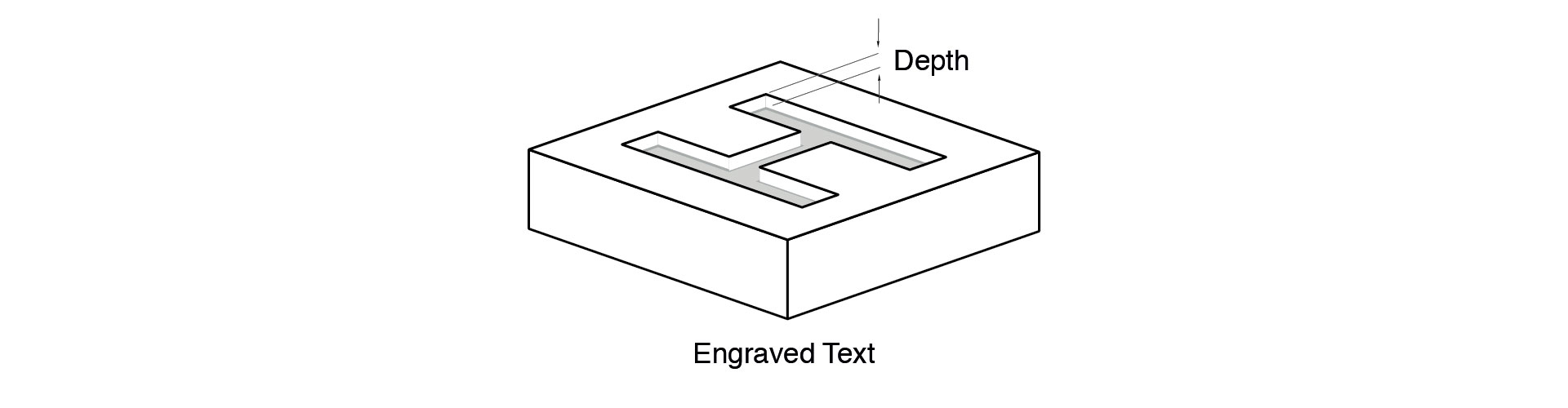
Engraved Details
An engraved detail is a recessed feature below the surface of a part. Because of the heat-dissipating from the laser into the surrounding powder during SLS, text and engraved details are at risk of closing up and won’t be visible if not designed with a minimum depth and width. Engraved details should be at least 1mm deep and 1mm wide.
Text
For readability, ensure minimum font height is 2mm (font size 14) and suitable for every direction. Always opt for larger fonts. Sans serif font is recommended not only for legibility but also to reduce details.
Text that is cut out of the material is much less legible than text that protrudes from the material, as it is harder to remove material in SLS. As such, choose embossed over engraved text.
| Wall Thickness | 0.7mm-2mm; 1mm is recommended |
|---|---|
| Holes | Greater than 1mm in diameter |
| Escape Holes | At least 3.5mm in diameter; add multiple holes |
| Slots | At least 0.5mm (depends on wall thickness and depth) |
| Pins | At least 0.8mm (depends on pin height) |
| Mating Parts | At least 0.5mm apart |
| Large, Flat Surfaces | Avoid whenever possible |
| Text | Minimum font height of 2mm; opt for larger fonts |
| Embossed Details | Minimum embossing height of 1mm |
| Engraved Details | Minimum engraving depth of 1mm and width of 1mm |
In this section, we outline some simple tips and tricks to help reduce the overall cost of your SLS part. In 3D printing, there are three main drivers of cost to bear in mind: material, printing time, and post processing time.
Use the 3D Printing Design Guidelines to help design your parts for machining then export your 3D CAD files in an STL format. Have your designs ready? Submit your designs now to get a FREE quote. Our team of 3D printing experts are always available to provide on-hand support and recommendations to ensure your parts are print ready.
Discover more design guides below:
