Vacuum casting, also known as urethane casting, is a soft tooling method that delivers lower-volume parts with quality similar to injection moulding but with much short lead times. It is an excellent process for creating a small series of parts from a range of thermoplastics, rubbers and resins.

To take full advantage of this technology, it is important that your 3D model closely follows a set of geometric recommendations. This article provides an overview of vacuum casting and considerations of the process and basic & advanced design insights and practices.
The vacuum casting process involves three main stages. 1. Building a master model using 3D printing (via SLA or SLS) or CNC machining. 2. Building the silicone tool by pouring liquid silicone around the master model then curing it. 3. Pouring resin into the cavity to create a production-like replica. The process provides greater freedom and flexibility in producing parts compared to other manufacturing technologies.
Vacuum Casting Process Considerations
Characteristics of Vacuum Casting
| Maximum Size | Up to 3000mm |
|---|---|
| Materials | PA-like, PMMA-like, ABS-like, PC-like and more |
| Surface | No more than 60% of wall thickness |
| Average Mold Life | 10 runs |
Tolerances
At HLH, standard tolerances are controlled to ISO 2768 Coarse (C) for urethane casting. For features left unspecified, standard tolerances are used. Tighter tolerances can be achieved, but is only recommended for critical features.
Wall Thickness
With vacuum casting, both thin and thick wall sections can be designed in the same part without impacting the final component. This allows for greater design freedom. Nevertheless, as part of good practice, consistency is recommended. At HLH, we suggest using a minimum wall thickness of 1mm.
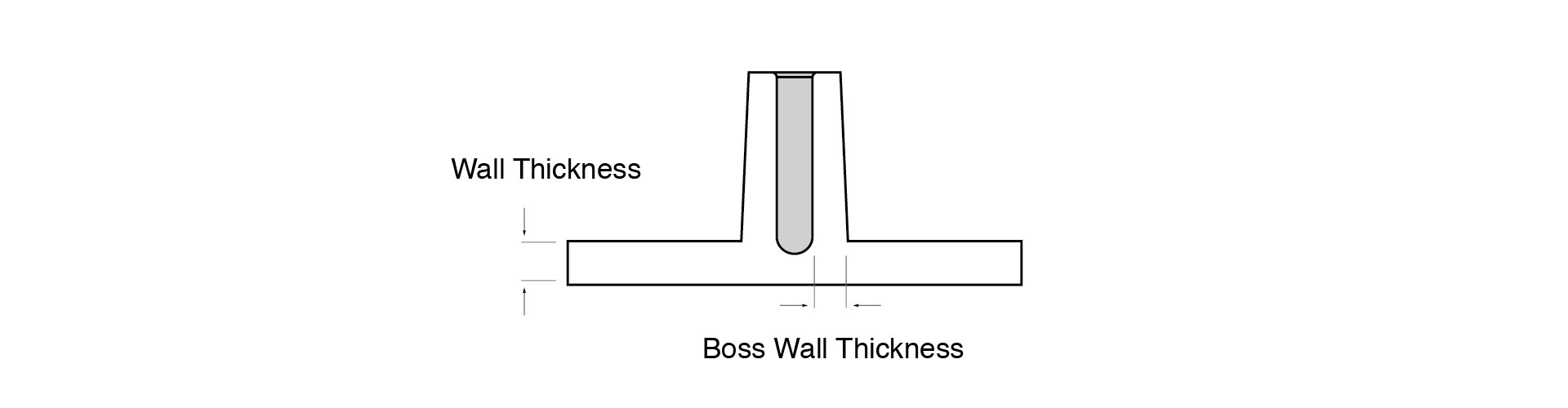
Bosses
Bosses should have a minimum height and diameter of 1mm, and wall thickness for bosses should be no more than 60 percent of the nominal thickness to minimise sinking.
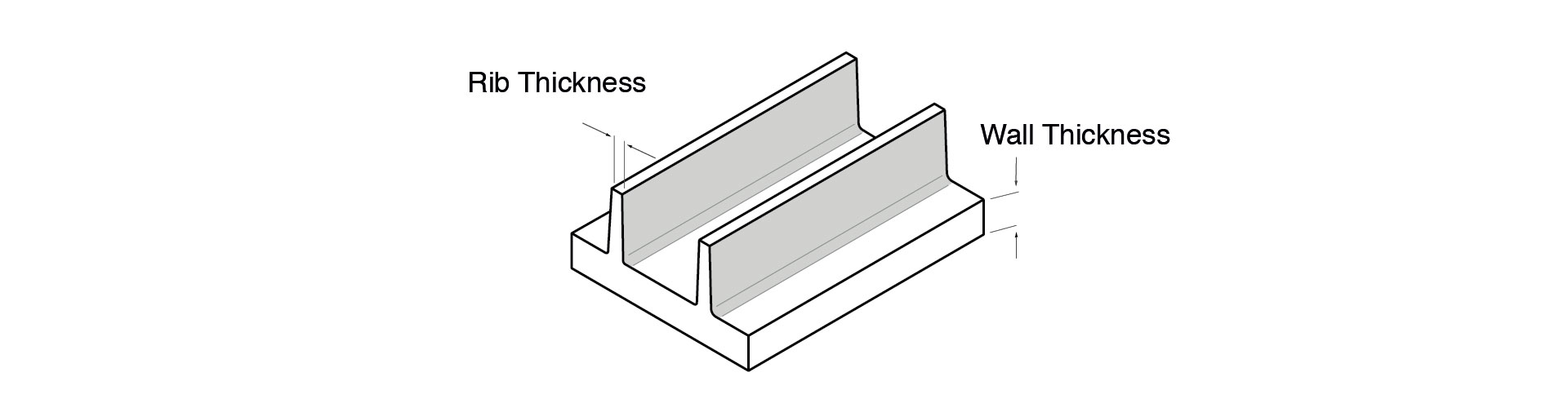
Ribs
Ribs can be added to large flat areas for strength and to reduce warping. Rib thickness should be less than wall thickness to minimise shrink and sinking effects. Experts recommend that rib thickness be no more than 60 percent of the nominal wall thickness, and the rib height should be limited to less than three times its thickness.
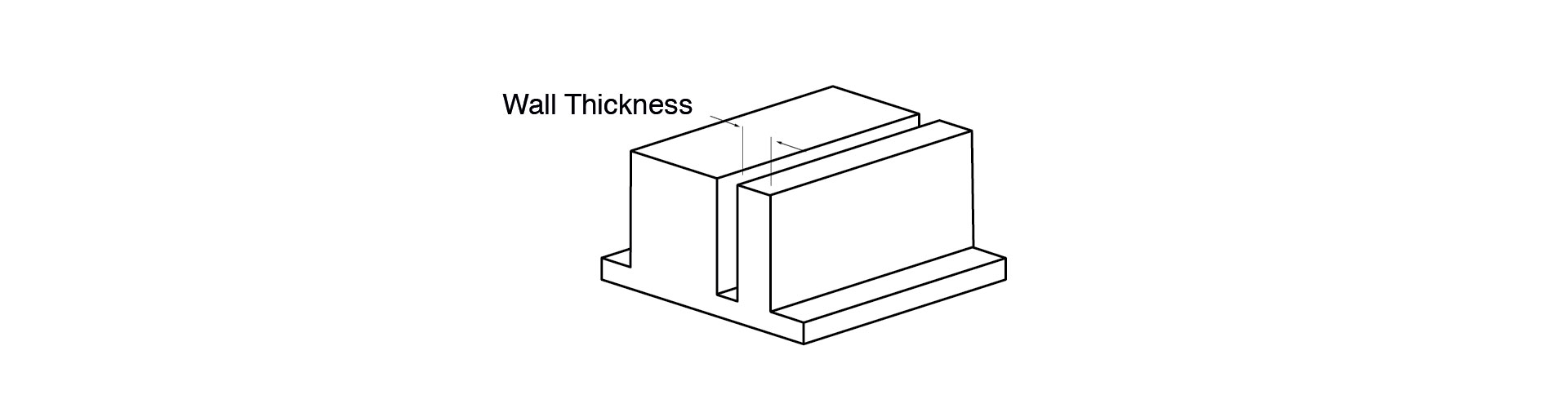
Undercuts
Undercuts are not a problem when designing for vacuum casting itself and can be done without inserts. However, if you’re building prototypes that are intended to move on to another production method like injection moulding where hard tooling is required, you should create your design as intended for production.

Embossed Details
Text and logos that are either recessed or embossed should be designed with a minimum depth/height of 1mm and width of 1mm to ensure visibility. For best results, leave a 1mm gap between letters.

| Wall Thickness | At least 1.0mm |
|---|---|
| Bosses | Minimum height of 1.0mm; minimum diameter of 1.0mm |
| Wall Thickness For Bosses | No more than 60% of wall thickness |
| Rib Thickness | No more than 60% of wall thickness |
| Rib Height | No more than 3x of rib thickness |
| Engraved and Embossed Details | Minimum depth of 1.0mm; minimum width of 1.0mm |
